List of Contents
What is the Floating Liquefied Natural Gas (FLNG) Terminals Market Size?
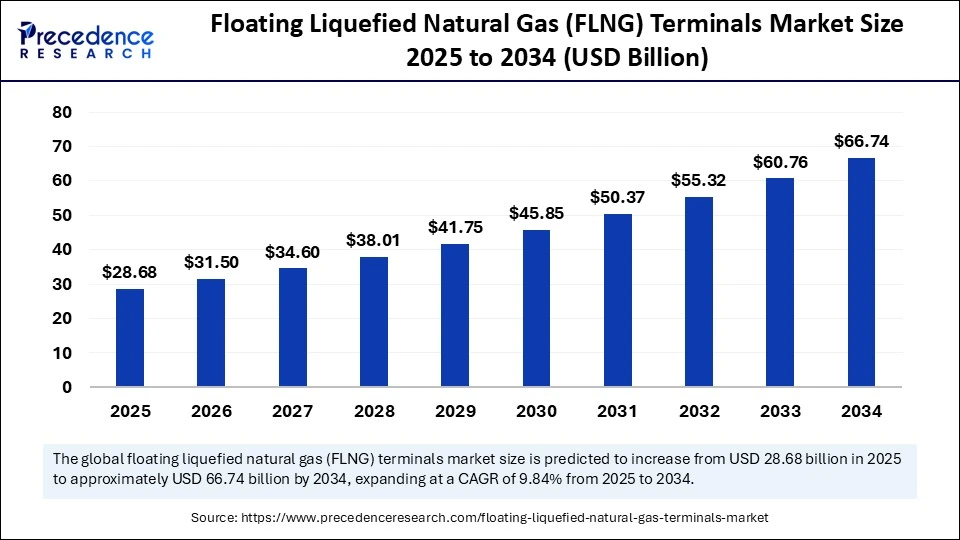
The global floating liquefied natural gas (FLNG) terminals market size is calculated at USD 28.68 billion in 2025 and is predicted to increase from USD 31.50 billion in 2026 to approximately USD 66.74 billion by 2034, expanding at a CAGR of 9.84% from 2025 to 2034. The global floating liquefied natural gas (FLNG) terminals market is driven by rising offshore gas exploration, energy demand, and advancements in modular and sustainable LNG technologies.
Market Highlights
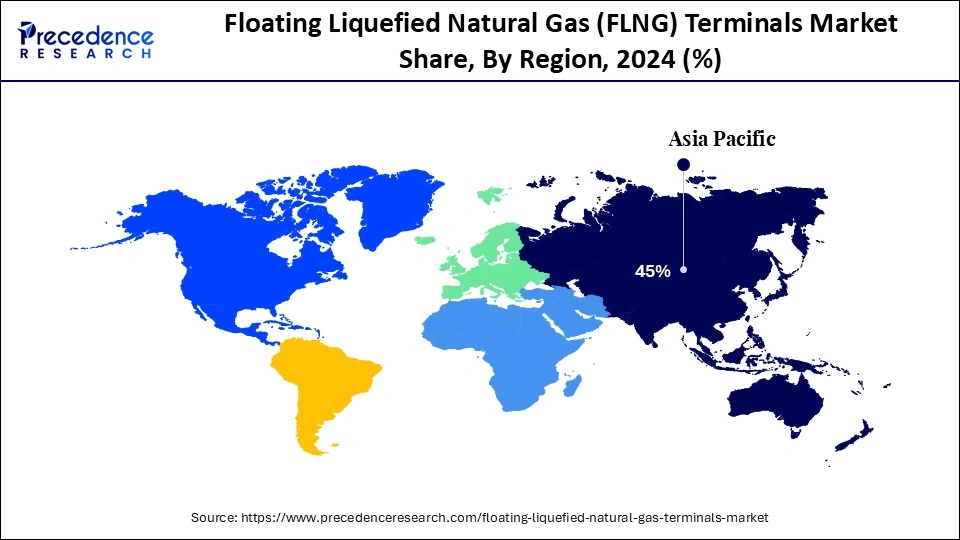
- Asia Pacific led the floating liquefied natural gas (FLNG) terminals market holding more than 45% of market share in 2024.
- The Middle East & Africa is estimated to expand the fastest CAGR between 2025 and 2034.
- By terminal type / asset, the floating storage and regasification units (FSRUs) segment held the major market share of 55% in 2024.
- By terminal type / asset, the floating LNG production vessels segment is growing at the fastest CAGR between 2025 and 2034.
- By contract type/ business model, the lease / hire contracts segment contributed the highest market share of 48% in 2024.
- By contract type/ business model, the build-own-operate models segment is expanding at a strong CAGR from 2025 to 2034.
- By application / end-use, the LNG export terminals segment accounted for the largest market share of 50% in 2024.
- By application / end-use, the regasification for the marine / bunkering segment is growing at a notable CAGR between 2025 and 2034.
- By capacity / module size, the large-scale (> 1,000,000 tpa) segment captured more than 60 % of market share in 2024.
- By capacity / module size, the mid-scale (500k1 M tpa) segment is expected to expand at a notable CAGR from 2025 to 2034.
Floating LNG Terminals Redefining Offshore Energy Logistics
The rising global demand for cleaner energy and an increasing need for cost-effective offshore gas processing solutions has created a new FLNG terminal market. An FLNG terminal is capable of liquefying, storing, and offloading natural gas at sea (at the point of liquefaction) while shifting away from dependence on land-based infrastructure. These floating units give operators flexibility, lower up-front capital costs, and faster deployment, making them ideal for remote or deep-water gas reserves.
Investment in modular and large capacity FLNG vessels is growing in the market, driven by increasing technological advancements and energy transition ambitions. In conclusion, FLNGs are set to change global LNG supply chains through efficiency and scalability in a growing demand market.
AI Anchors the Future: How Intelligent Systems Are Revolutionizing Floating LNG Terminals
With sensors becoming an integral part of analytics in the operational landscape of floating LNG (FLNG) terminals, operators now implement advanced artificial intelligence to facilitate improvements in safety and efficiency. For example, as highlighted in an industry case study in August 2025, an LNG terminal was using AI-enabled tools to monitor heat-exchanger pressure fluctuations to identify early-stage fouling long before alarms needed to be activated.
For FLNG operators and assets, the ability to implement data interfaces for real-time analytics, predictive maintenance strategies, and modelling equipment-health instills more uptime, extended asset-life, and safety in remote offshore environments. These changes in expectations indicate a larger trend - as floating LNG terminals scale-up and take on increasingly complicated operations, monitoring with the aid of AI will be part of obtaining next-generation solutions.
- In September 2025, Invenire Petrodyne Limited and Excelerate Global Operations LLC, launched the first-of-its-kind New floating LNG terminal project in the Haldia Dock Complex, Kolkata to introduce AI for oil terminal use; improving vessel turnaround time from three hours to forty-five seconds, achieving twenty percent increased utilization of the jetty.
Key Technological Shifts in the Floating Liquefied Natural Gas (FLNG) Terminals Market
Smart and Sustainable: Tech Innovations Driving FLNG Terminals ForwardIn the dynamic environment of floating liquefied natural gas (FLNG) terminals, sustainability is becoming a central theme that drives technological advancement. Operators like PETRONAS have put into practice energy efficient power systems and zero-flaring practices on-board of its FLNG units, successfully lowering fuel consumption and reducing greenhouse gas emissions. Firms like Keppel Offshore & Marine have shown that the retrofitting of an LNG carrier into an FLNG vessel can reduce lifecycle emissions by around one-third compared to building a new vessel.
Meanwhile, projects like the Coral Sul FLNG in deep-water offshore Mozambique is not only expanding the use of LNG but also demonstrating local-content and efficiency designs into the overall project to advance the energy transition. These innovations, taken together, indicate a transformation in the development of a floating liquefied natural gas (FLNG) terminal, moving from simply an expansion of capacity to integrated solutions more strongly aligned with both the carbon impact and social impact.
Floating Liquefied Natural Gas (FLNG) Terminals Market Outlook
The FLNG terminal industry is experiencing strong momentum as governments redirect focus toward monetizing their offshore gas supply in innovative and flexible LNG infrastructure. Supported by government energy transition policies, FLNG terminals enable rapid execution and utilization of gas in gas fields globally, contributing to reliable and long term capacity expansion.
Global FLNG infrastructure is growing in the Asia Pacific region, Africa, and North America, as governments place increased emphasis on energy diversification and securing LNG imports. Efforts to develop offshore liquefaction facilities offer improved trading efficiency in cross-border markets, thus enabling reduced dependence on fixed and onshore facilities while increasing global connections for gas transaction.
Research and development continues to enhance the dynamics of modular liquefaction technologies, cryogenic systems, and digital monitoring of FLNG processes and operations. The advancement of hull design, optimization of storage, and design features to recovery energy continue to increase the cost-effectiveness, environmental impact, and reliability of offshore gas processing facilities.
FLNG projects involve the design features of low carbon, for example, carbon capture readiness, recovery of waste heat, and energy-efficient liquefaction processes. The focus of government to decarbonize LNG value chains may lead to investment in FLNG technologies to support cleaner, low-carbon fuel, consequently supporting a net-zero transition.
There are a few key drivers, including an increase in worldwide natural-gas demand (mainly in the industrial and power markets), continuing to develop offshore reservoirs, and using flexible terminal deployment to reduce the lead-times associated with on-shore builds.
High upfront investment, long regulatory approval cycles, offshore engineering risks, and possible demand saturation are significant constraints, especially if LNG supply growth exceeds demand in some areas.
Market Scope
| Report Coverage | Details |
| Market Size in 2025 | USD 28.68 Billion |
| Market Size in 2026 | USD 31.50 Billion |
| Market Size by 2034 | USD 66.74 Billion |
| Market Growth Rate from 2025 to 2034 | CAGR of 9.84% |
| Dominating Region | Asia Pacific |
| Fastest Growing Region | Middle East & Africa |
| Base Year | 2025 |
| Forecast Period | 2025 to 2034 |
| Segments Covered | Terminal Type / Asset, Contract Type / Business Model, Application / End-Use, Capacity / Module Size, and Region |
| Regions Covered | North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, Latin America, and Middle East & Africa |
Floating Liquefied Natural Gas (FLNG) Terminals MarketSegments Insights
Terminal Type/Assset Insights
Floating Storage and Regasification Units (FSRUs) account for 55% of the FLNG terminal market. Their relatively lower deployment costs in comparison with fixed costs and their ability to increase gas supply with security makes them a favoured option for both developing and gas import nations. Additionally, they can easily be scaled and commissioned more quickly than onshore facilities.
Floating LNG Production Vessels (FLNGs) are the fastest growing sector of the gas industry because they continue to grow in popularity for monetizing offshore gas fields. They allow liquefaction to take place directly at sea, which reduces the necessity for expensive and challenging offshore or onshore pipeline and infrastructure. The continued focus on developing deep-water gas reserves and remote fields is sustaining FLNG demand.
Floating LNG Liquefaction Platforms are becoming popular for smaller applications. Physical characteristics include turret mooring or fixed offshore. These platforms combine production; liquefaction and storage in one unit and can efficiently liquefy stranded gas fields. Although smaller in scale, their use can increase efficiency and provide greater flexibility to offshore LNG applications.
Contract Type / Business Model Insights
Lease/Hire Contracts: The Lease or hire contracts segments dominated the market with a share of approximately 48% due to their cost effective solution and risk-sharing situation. Lease or hire contracts allow operators to gain access to FLNG assets, without significant upfront capital investment. The combination of flexibility and speed to market appeals to energy companies, specifically those looking for cost-efficacy who have quick access to more volatile LNG regional demand.
Build-Own-Operate Models: Build-Own-Operate (BOO) agreements are experiencing the strongest growth, as energy majors and private operators invest in long-term infrastructure for the development of LNG. This ensures operators have operational control of the asset or vessel and can generate higher profits in the long-run. Increased demand for LNG from the electricity and industrial markets challenges direct ownership as a way to establish a stable supply chain of LNG.
Joint Ventures and Public-Private Partnerships (PPP): Joint Ventures and Public-Private Partnerships (PPP) are becoming increasingly common in projects with significant infrastructure. These contracts ensure shared capital contribution, the ability to partner and share technology and risk-sharing, with national governments and private developers, notably in developing coastal markets exploring offshore LNG.
Application / End Use Insights
LNG Export Terminals: LNG Export Terminals lead the segment with about 50% market share, driven by increasing production from offshore reserves and the desire to serve the international demand. These terminals facilitate large-scale LNG exports from resource-rich countries to energy-deficit areas, supporting continuous trade flows.
Regasification for Marine/Bunkering: Regasification for Marine and Bunkering applications is the fastest-growing use case as the shipping industry transitions toward cleaner fuels. The increase in the number of LNG-powered vessels and the implementation of global emissions regulations are driving the adoption of floating regasification solutions for all maritime operations.
LNG Import Terminals: LNG Import Terminals play an important supporting role in the global energy chain. They help diversify energy supplies and assist nations in making advances in energy resilience. Portable and modular import units allow countries with limited infrastructure to meet their domestic gas needs in an efficient manner.
Capacity/Module Size Insights
Large scale (>1,000,000 tpa): Large-scale (>1,000,000 tpa), is made up of regular LNG FLNG, which has dominated the market with about 60% of the total capacity. It offers the advantages of size that allow for flexibility and economies of scale, and the greater operational cost efficiency associated with handling high volumes. This is complemented by export markets for regional- and global LNG, as well as meeting LNG contracts for the duration of the production life cycle.
Mid scale capacity (500,000-1,000,000) is the most rapid growth expanded. They are seen as a middle ground for overall investment and cost efficiency with production flexibility. Mid-scale is ideal for smaller offshore or regional projects and associated marine or pipeline infrastructures. These intermediate installations offer suitable throughput, without the upfront capital intensive nature of larger fixed terminal facilities.
Small-scale (<500,000 tpa) Small scale systems offer increased flexibility for isolated or low-demand market areas. Most companies use small scale systems for either decentralized power generation, niche industrial consumers, or more commonly in regional gas distribution channels, meanwhile improving access to clean energy in rural and remote areas.
Floating Liquefied Natural Gas (FLNG) Terminals MarketRegional Insights
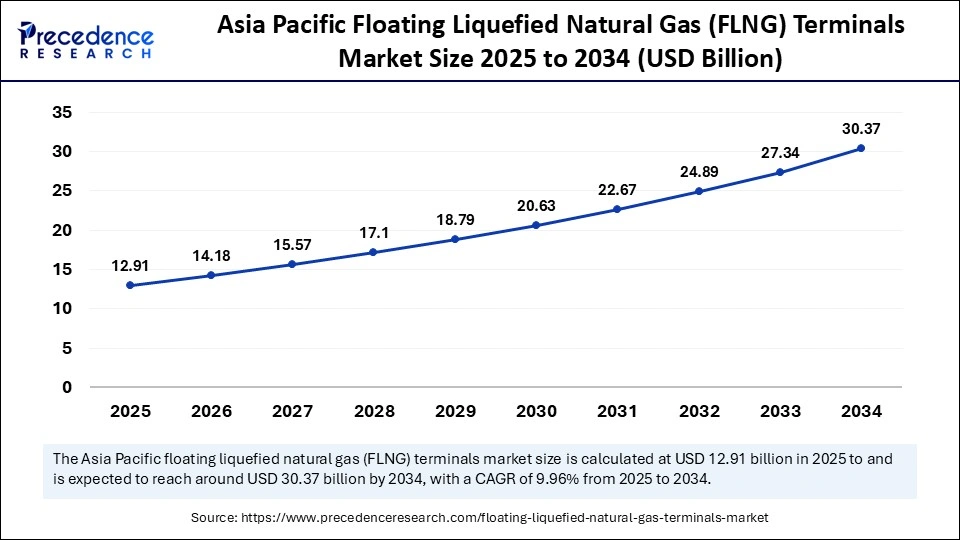
The Asia Pacific floating liquefied natural gas (FLNG) terminals market size is expected to be worth USD 30.37 billion by 2034, increasing from USD 12.91 billion by 2025, growing at a CAGR of 9.96% from 2025 to 2034.
What Makes Asia Pacific The Leading Region for the Floating Liquefied Natural Gas (FLNG) Terminals Market?
Asia Pacific leads as it pools the largest incremental gas demand with coastal restrictions that make floating solutions quicker and cheaper than large on-shore terminals. The IEA suggests that around half of total demand growth for gas globally out to 2030 is expected to originate in Asia Pacific, placing import needs in coastal economies utilizing modular FSRUs and floating import terminals as solutions to the urgent needing of electricity and industrial demand for gas. Recent policy pushes and active project pipelines in Southeast and South Asia have encouraged buyers to prefer a short lead time and leaseable floating asset which mitigates capex risk and speed up security of supply.
India Floating Liquefied Natural Gas (FLNG) Terminals Market Trends
India typifies the region adoption to FLNG: the national appetites for multiple FSRU and hybrid floated-plus-land projects are driven on plans to expand LNG import capacity and pipeline connectivity. In October 2025, Adani Ports and Special Economic Zone (APSEZ) partnered with Bharat Petroleum Corporation (BPCL) to start Indias first ship-to-ship liquefied natural gas (LNG) foundation facility at Vizhinjam International Seaport, Kerala.
From a business perspective, Indias strategy serves to reduce permitting timelines, spreads investment timelines, and provides association between floating and national pipeline deployments making the country a focal point for charterers, EPCs and vessel.
Floating LNG (FLNG) Terminal Projects in Asia Pacific
| Country | Project | Type (FLNG/FSRU) | Capacity/Notes | Estimated Commissioning | Developer/Contractor |
| Indonesia | West Papua (Kasuri Block) | FLNG | 1.2 Mtpa | Q2 2026 | Wison New Energies for Genting Oil & Gas |
| India | Haldia Dock, West Bengal | FSRU + land-regasification | Initial 1.5 MMTPA, expandable to 3 MMTPA | H2 2027 | Excelerate Global & Invenire Petrodyne |
| Singapore | Jurong Port/second import terminal | FSRU | Storage 200,000 m, 5 Mtpa regas capacity | Not Specified | Mitsui O.S.K. Lines (MOL) |
| Singapore | Jurong Port FSRU | FSRU/floating import terminal | LNG storage 200,000 m; regasification capacity 5 Mtpa | Unit delivered in 2027 | Mitsui O.S.K. Lines (owner) built by Hanwha Ocean in Collaboration with ABB |
| China (Build) / Africa (Deployment) | Nguya FLNG | FLING (Floating Liquefaction) | 2.4 Mtpa liquefaction; LNG storage capacity 180,000 m | sail away in September 2025 | Wison New Energies, for Eni S.p.A. |
| Australia | Port Kembla LNG import terminal | FSRU | 170,000 m FSRU for terminal | 2026 | Squadron Energy |
What Is Driving Middle East & Africa To Be The Fastest Growing Region?
The Middle East and Africa region is experiencing the most significant growth in the floating liquefied natural gas (FLNG) terminals market, fueled by increased demand for domestic gas consumption, large untapped offshore reserves, and export aspirations. Some African countries are already pursuing floating solutions to monetise stranded offshore gas reserves, utilising the simplicity of floating solutions that do not require significant capital investment and lengthy construction time associated with onshore facilities. The regulatory flexibility in the region and the strategic proximity to Europe make it an ideal relocation hub for LNG trading and re-export activities.
Egypt Floating Liquefied Natural Gas (FLNG) Terminals Market Trend
Egypt distinguishes itself as the foremost country in the realm of floating LNG terminals in both the Middle East and Africa, as it serves as both an exporter and an importer. Egypt is currently developing its floating regasification capacity to secure domestic supply reliability in light of uncertain upstream production.
- In May 2025, the Egyptian Natural Gas Holding Company ("EGAS") entered into a 10-year charter with Hoegh LNG for the Hoegh Gandria, a floating storage and regasification unit to be stationed at Ain Sokhna Port, with a capability to deliver up to 1,000 million standard cubic feet per day.
Simultaneously, Egypt is upgrading LNG export facilities at Damietta and Idku to facilitate flexible floating liquefaction. All of this is contingent to Egypts strategy to serve as a significant hub for LNG redistribution between the Middle East, Africa, and Europe.
The floating liquefied natural gas (FLNG) terminals market in North America is experiencing positive expansion and growth trends due to its abundance of natural gas reserves, rising export capability, and willingness for flexible offshore infrastructure. The region is focusing on export-based initiatives to monetize shale gas production while minimizing reliance on onshore terminals. North America also has robust shipbuilding capabilities, increasing government support for exporting low-emission energy, and growing investments from Indigenous and private entities. These developments position North America as an increasingly important player in the global FLNG expansion market.
U.S. Floating Liquefied Natural Gas (FLNG) Terminals Market Trends
The U.S. is strengthening its global leadership in the floating LNG (FLNG) terminal market by evolving from an exporter to a technology and infrastructure provider. This was illustrated on October 28, 2025, when Excelerate Energy, a Texas-based LNG company, announced a $450 million deal to build a fully integrated FLNG import terminal in Iraq.
This is a relevant example of how U.S. companies are utilizing domestic expertise in floating storage and regasification units (FSRUs) to assist energy-deficient countries. With respect to the Iraq FLNG project, the project includes the FSRU and other terminal equipment, which reflects the U.S. capability to provide the entire FLNG solution abroad.
Quick Picks by Regional Insights Floating Liquefied Natural Gas (FLNG) Terminals Market
| Company | Country | Product/Project | Uses/Purpose |
| Shell plc | U.K. / Netherlands | Prelude FLNG | One of the worlds largest floating LNG facilities, designed to extract, liquefy, store, and offload natural gas directly at sea. |
| Petronas | Malaysia | PFLNG Satu & PFLNG Dua | Pioneering offshore LNG units that enable gas liquefaction from deepwater fields, expanding Malaysias LNG export capacity. |
| Exmar NV | Belgium | Tango FLNG | Compact and relocatable FLNG unit designed for small- to mid-scale LNG production and export, currently deployed in Argentina. |
| Golar LNG Limited | Bermuda | Hilli Episeyo FLNG | Converted LNG carrier providing floating liquefaction services off Cameroon; supports flexible LNG monetization for stranded gas fields. |
| Hyundai Heavy Industries (HHI) | South Korea | FLNG Engineering & Construction Solutions | Designs and builds large-scale FLNG hulls and topsides, supplying global energy companies with turnkey floating LNG infrastructure. |
| Samsung Heavy Industries (SHI) | South Korea | FLNG Vessel Fabrication | Manufactures advanced FLNG vessels and FPSO conversions, integrating liquefaction modules for major oil and gas clients. |
| Technip Energies | France | FLNG Process & Engineering Solutions | Provides FEED and EPC services for floating LNG projects, specializing in modular liquefaction and energy-efficient designs. |
Floating Liquefied Natural Gas (FLNG) Terminals Market Value Chain
The beginning of an FLNG operation involves the extraction of natural gas offshore. Subsea wells and riser pipelines transport gas to the vessel, creating a consistent supply from distant offshore reservoirs of natural gas for following processing and liquefaction.
Once on board FLNG vessels, raw gas is purified by removing water, CO₂, and sulfur. The liquefaction process cools the gas to -162�C through cryogenic processes which creates LNG as the gas occupies 1/600th of its volume in a gaseous state.
Once liquefied, natural gas is stored in specialized insulated cryogenic tanks on the vessel. Once the tanks are full, the LNG is offloaded into LNG carriers through a specialized LNG loading platform to ensure safe and efficient transfer.
Once offloaded into an LNG carrier, LNG is transported through international waters to import terminals connected to the natural gas pipeline system. This phase of the supply chain involves temperature-controlled storage and managing boil-off time during transportation to ensure safe and healthy natural gas quality once transferring the LNG to regasification facilities.
At the receiving terminal or FSRU, LNG is prepared to be turned back into natural gas. Once in the appropriate condition, the natural gas is injected into the natural gas distribution pipeline for industrial use, power generation and residential use of energy supply, therefore completing a FLNG supply chain from extraction to final use.
Floating Liquefied Natural Gas (FLNG) Terminals Market Companies
- Headquarters: London, United Kingdom
- Year Founded: 1907
- Ownership Type: Publicly Traded (LSE: SHEL; NYSE: SHEL)
History and Background
Shell plc was formed in 1907 through the merger of the Royal Dutch Petroleum Company and the Shell Transport and Trading Company of the United Kingdom. Over more than a century, Shell has evolved into one of the worlds largest energy corporations, operating across oil, natural gas, chemicals, and renewable energy sectors.
In the Floating Liquefied Natural Gas (FLNG) Terminals Market, Shell is a recognized pioneer, having developed and operated Prelude FLNG, the worlds first large-scale floating liquefied natural gas facility. Prelude marked a major milestone in offshore gas production, enabling the liquefaction, storage, and offloading of LNG directly at sea. Shell continues to lead innovation in FLNG technology, focusing on energy efficiency, carbon reduction, and modular floating production systems.
Key Milestones / Timeline
- 1907: Formation of Royal Dutch Shell Group
- 2011: Announced development of Prelude FLNG, the first commercial-scale FLNG facility
- 2017: Commenced production at Prelude FLNG offshore Western Australia
- 2022: Strengthened focus on low-carbon LNG and digital optimization for floating assets
- 2025: Advanced studies for next-generation FLNG units with enhanced efficiency and smaller modular design
Business Overview
Shell operates as a global energy company engaged in exploration, production, refining, and marketing of oil and gas, as well as renewable and low-carbon energy solutions. Within the FLNG market, Shell focuses on designing, constructing, and operating floating LNG production units that enable offshore monetization of stranded gas fields. Prelude FLNG remains the flagship project representing Shells technological leadership in this field.
Business Segments / Divisions
- Integrated Gas and LNG
- Upstream Exploration and Production
- Downstream and Chemicals
- Renewables and Energy Solutions
Geographic Presence
Shell operates in more than 70 countries with major LNG and FLNG operations in Australia, Qatar, Nigeria, and the United States.
Key Offerings
- Prelude FLNG-Worlds first commercial-scale floating LNG production unit
- LNG supply, storage, and regasification services
- FLNG technology and modular design expertise
- Digital monitoring systems for floating asset management
Financial Overview
Shell reports annual revenues exceeding $350 billion USD, with LNG and integrated gas operations contributing significantly to profitability. The FLNG segment represents a strategic growth area within Shells transition toward cleaner and more flexible natural gas infrastructure.
Key Developments and Strategic Initiatives
- January 2023: Initiated study on next-generation FLNG vessels to reduce carbon intensity by 30%
- October 2023: Enhanced digital operations management for Prelude FLNG using AI and predictive analytics
- April 2024: Expanded global partnerships to develop smaller, cost-efficient FLNG designs
- February 2025: Began conceptual design work for modular mid-scale FLNG facilities in Asia-Pacific
Partnerships & Collaborations
- Collaboration with Technip Energies and Samsung Heavy Industries for FLNG design and construction
- Partnership with Petronas and Inpex for offshore LNG project development
- Cooperation with government and energy regulators for sustainable FLNG deployment
Product Launches/Innovations
- Prelude FLNG facility (2017)
- Digital twin platform for FLNG asset optimization (2024)
- Modular mid-scale FLNG concept design (2025)
Technological Capabilities/R&D Focus
- Core technologies: FLNG liquefaction systems, modular construction, cryogenic storage, and predictive asset monitoring
- Research Infrastructure: Shell Technology Centres in the Netherlands, United Kingdom, and Singapore
- Innovation focus: Smaller, efficient, low-carbon FLNG systems integrating renewable power and advanced process controls
Competitive Positioning
- Strengths: Global LNG leadership, proprietary FLNG technology, strong operational experience
- Differentiators: First-mover advantage in large-scale FLNG and integrated value chain from production to marketing
SWOT Analysis
- Strengths: Industry leadership, strong financial position, advanced FLNG technology
- Weaknesses: High capital cost and complexity of FLNG projects
- Opportunities: Growth in offshore gas monetization and modular FLNG demand
- Threats: LNG price volatility and regulatory pressures on emissions
Recent News and Updates
- June 2024: Shell announced upgrades to Prelude FLNG to enhance energy efficiency and reduce flaring
- October 2024: Entered new FLNG partnership feasibility study with Petronas for Asia-Pacific expansion
- January 2025: Began early-stage design studies for a next-generation carbon-efficient FLNG platform
- Headquarters: Hamilton, Bermuda
- Year Founded: 1946
- Ownership Type: Publicly Traded (NASDAQ: GLNG)
History and Background
Golar LNG Ltd. traces its origins to 1946 as Gotaas-Larsen Shipping Company and later evolved into one of the leading independent owners and operators of LNG carriers and floating LNG infrastructure. In the early 2000s, Golar strategically shifted its focus toward Floating Liquefied Natural Gas (FLNG) and Floating Storage and Regasification Units (FSRUs), pioneering flexible solutions for LNG production and import operations.
Golar has since established itself as a major innovator in the FLNG terminals market, with multiple successful projects including Hilli Episeyo (offshore Cameroon), the worlds first converted FLNG vessel, and ongoing development of Gimi FLNG in partnership with BP offshore Mauritania and Senegal. The company focuses on cost-effective FLNG conversions and scalable floating production units, offering lower capital intensity than traditional onshore LNG facilities.
Key Milestones / Timeline
- 1946: Founded as Gotaas-Larsen Shipping Company
- 2001: Listed on NASDAQ as Golar LNG Ltd.
- 2018: Commissioned Hilli Episeyo FLNG, the worlds first LNG carrier-to-FLNG conversion
- 2022: Advanced construction of Gimi FLNG for BPs Greater Tortue Ahmeyim project
- 2024: Announced plans to expand modular FLNG fleet to meet global gas demand
- 2025: Began evaluation of next-generation FLNG conversions for new African and Asian offshore fields
Business Overview
Golar LNG specializes in developing and operating floating LNG liquefaction, storage, and regasification assets. The company business model emphasizes FLNG vessel conversion, leveraging existing LNG carriers to reduce cost and construction time compared to greenfield onshore facilities. Golars assets serve the entire LNG value chain from gas capture and liquefaction to transportation and regasification.
Business Segments/Divisions
- Floating Liquefied Natural Gas (FLNG)
- Floating Storage and Regasification Units (FSRUs)
- LNG Carrier Operations
- Engineering, Procurement, and Project Development
Geographic Presence
Golar LNG operates globally, with major projects and partnerships in West Africa, Latin America, Southeast Asia, and the Middle East.
Key Offerings
Converted and newbuild FLNG production vessels
Floating Storage and Regasification Units (FSRUs)
Engineering and operations for offshore LNG infrastructure
Midstream gas processing and monetization solutions
Financial Overview
Golar LNG reports annual revenues of approximately $400 to 500 million USD, driven by long-term FLNG and FSRU contracts. The company maintains steady profitability through recurring charter income and equity partnerships in major LNG projects.
Key Developments and Strategic Initiatives
- April 2023: Delivered first LNG cargo from Hilli Episeyos upgraded production capacity
- October 2023: Progressed commissioning of Gimi FLNG for BPs Mauritania-Senegal project
- March 2024: Announced feasibility studies for two new FLNG conversion projects in West Africa
- January 2025: Initiated partnerships to develop smaller, modular FLNG units for offshore Asia
Partnerships & Collaborations
- Strategic partnership with BP for Greater Tortue Ahmeyim FLNG project
- Collaborations with Keppel Shipyard for FLNG conversions
- Alliances with energy companies for floating LNG production and gas monetization initiatives
Product Launches/Innovations
- Hilli Episeyo FLNG (2018) Worlds first converted FLNG vessel
- Gimi FLNG (2024) - Large scale offshore liquefaction vessel
- Next-generation modular FLNG design program (2025)
Technological Capabilities / R&D Focus
- Core technologies: LNG carrier conversion, liquefaction modules, cryogenic systems, and modular FLNG design
- Research Infrastructure: Engineering collaborations with Keppel Shipyard and industry partners in Singapore
- Innovation focus: Cost-efficient FLNG conversions, modular liquefaction plants, and scalable floating energy solutions
Competitive Positioning
- Strengths: Proven FLNG conversion technology, flexible deployment, lower capital costs
- Differentiators: Experience in rapid deployment of cost-effective floating LNG units
SWOT Analysis
- Strengths: First-mover advantage in FLNG conversions, operational efficiency, strategic partnerships
- Weaknesses: Limited scale compared to supermajors like Shell
- Opportunities: Growing demand for offshore gas liquefaction and midstream LNG infrastructure
- Threats: Technical risks, LNG market fluctuations, and geopolitical challenges in offshore regions
Recent News and Updates
- February 2024: Golar announced successful sea trials for Gimi FLNG unit
- August 2024: Signed memorandum of understanding for modular FLNG development in Southeast Asia
- January 2025: Delivered upgraded Hilli Episeyo FLNG capacity and initiated feasibility study for next-generation conversion project
Other Companies in the Market
- Samsung Heavy Industries Co, Ltd. (SHI): SHI designs and constructs large-scale FLNG vessels and LNG carriers, including the hull fabrication for Shells Prelude FLNG. The company offers engineering, procurement, and construction (EPC) services for offshore LNG and FPSO platforms, leveraging advanced shipbuilding capabilities and automation technology.
- Hyundai Heavy Industries Holdings Co., Ltd. (HHI): HHI specializes in the construction of FLNG hulls, LNG carriers, and offshore modules, offering turnkey EPC solutions. The companys advanced LNG containment systems and cryogenic technologies enhance the efficiency and safety of FLNG units. HHI plays a major role in the global offshore energy infrastructure market.
- TechnipFMC plc: TechnipFMC delivers integrated subsea and surface FLNG solutions, including engineering, procurement, and project management for offshore LNG facilities. The company has been involved in major FLNG projects like Coral South FLNG (Mozambique), providing topside engineering and process modules. Its strength lies in integrated offshore processing and liquefaction systems.
- MODEC, Inc.: MODEC provides floating production systems, including FPSOs and FLNG conversion expertise. The company offerings include the design, leasing, and operation of floating units for gas monetization. MODECs modular FLNG platforms are designed for cost efficiency and operational reliability in remote gas fields.
- BW Offshore Ltd.: BW Offshore focuses on floating production, storage, and offloading (FPSO) and FLNG conversion projects, providing turnkey design and operational services. The company leverages its FPSO expertise to deliver mid-scale FLNG units that offer flexibility and rapid project deployment for offshore gas developments.
- Chevron Corporation: Chevron has significant interests in offshore LNG and floating gas production, including partnerships in projects like Wheatstone LNG and Prelude FLNG. The company upstream and midstream integration enables efficient gas monetization strategies, with ongoing investments in FLNG feasibility and carbon-efficient liquefaction technologies.
- Petrofac Limited: Petrofac provides EPC and project management services for FLNG terminals, offering engineering design, topside integration, and offshore commissioning support. The companys focus on modular construction and digital engineering enhances project execution efficiency in floating LNG applications.
- McDermott International, Inc.: McDermott is a leading EPC contractor for offshore LNG infrastructure, specializing in FLNG topside modules, subsea integration, and cryogenic systems. The company has supported several key FLNG developments in Africa and Asia, emphasizing end-to-end delivery of complex floating facilities.
- Saipem S.p.A.: Saipem offers engineering, procurement, and construction solutions for both FLNG and FSRU (Floating Storage and Regasification Unit) projects. The companys experience spans from subsea gas systems to topside liquefaction modules. Saipem proprietary designs support both large-scale and modular FLNG development.
- KBR, Inc.: KBR provides FEED (Front-End Engineering Design) and project management consultancy for FLNG and LNG liquefaction facilities. The companys expertise in gas processing, LNG liquefaction, and floating system design makes it a preferred engineering partner for early-stage FLNG projects.
- Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd. (MHI): MHI delivers FLNG engineering and liquefaction process technologies, including LNG plant components, cryogenic compressors, and liquefaction modules. The company strong background in LNG carrier technology and marine systems supports efficient floating LNG deployment.
- Wartsila Corporation (Finland): Wartsila provides power, propulsion, and gas handling systems for FLNG and FSRU applications. Its integrated energy and marine solutions improve operational efficiency and reliability of floating LNG platforms. Wartsila also supports hybrid and sustainable power systems for offshore energy infrastructure.
- Cheniere Energy, Inc. (U.S.): While primarily known for onshore LNG terminals, Cheniere is expanding into floating LNG opportunities through collaborations that leverage its liquefaction technology and midstream expertise. Its focus on flexible LNG supply solutions positions it as an emerging player in floating LNG commercialization.
Recent Developments
- In June 2024Cedar LNG Partners LP announced a positive final investment decision (FID) for a floating LNG (FLNG) facility in British Columbia with nameplate 3.3 mtpa capacity, co owned by the Haisla Nation and Pembina Pipeline Corporation, powered by renewable electricity. (Source: https://www.cedarlng.com)
- In October 2025Eni S.p.A. and its partners announced the FID for the Coral North FLNG project offshore Mozambiques Rovuma Basin a project targeting 3.6 mtpa capacity and deep water FLNG deployment in Africa. (Source: https://egyptoil-gas.com)
- In October 2025Delfin Midstream Inc. awarded Samsung Heavy Industries an exclusive EPCI contract for the first of up to three FLNG vessels for its U.S. export project offshore Louisiana, in advance of a Final Investment Decision expected later in 2025.(Source: https://www.offshore-energy.biz)
Exclusive Insights
Our analysts observe that the floating liquefied natural gas (FLNG) terminals market is a game-changer in worldwide energy logistics, potentially enabling offshore gas monetization and lowering reliance on traditional onshore terminals. The market is anticipated to expand steadily in the coming years, as demand for flexible solutions for LNG production and import rises especially in regions without extensive pipeline infrastructure.
Nonetheless, high upfront capital costs, complicated regulatory approvals, and technical integration may hamstring quick deployment. Nevertheless, increasing investment in modular FLNG designs and carbon capture integration combined with digitization and digital monitoring systems is poised to create significant opportunities in the business space. New trends emerging in the FLNG market are smaller-scale FLNGs, partnerships as blueprints, and designs fueled by sustainability to optimize efficiency and bypass ecological harm.
Floating Liquefied Natural Gas (FLNG) Terminals MarketSegments Covered in the Report
By Terminal Type/Asset
- Floating LNG Production Vessels (FLNG)
- Floating Storage and Regasification Units (FSRUs)
- Floating LNG Liquefaction Platforms (offshore fixed or turret-moored)
By Contract Type/Business Model
- Build-Own-Operate (BOO)
- Lease / Hire (Time Charter / Charter-Out)
- Joint Venture / Public-Private Partnership (PPP)
By Application / End Use
- LNG Export Terminals
- LNG Import Terminals
- Regasification for Marine/Bunkering
- Offshore Gas Field Monetization
By Capacity / Module Size
- Small-scale (<500,000 tpa)
- Mid-scale (500,000-1,000,000 tpa)
- Large-scale (>1,000,000 tpa)
By Region
- North America
- Europe
- Asia-Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East and Africa
For inquiries regarding discounts, bulk purchases, or customization requests, please contact us at sales@precedenceresearch.com
Frequently Asked Questions
Ask For Sample
No cookie-cutter, only authentic analysis – take the 1st step to become a Precedence Research client



